1 中国科学院光电技术研究所微细加工光学技术国家重点实验室,四川 成都 610209
2 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
3 中国科学院光电技术研究所矢量光场研究中心,四川 成都 610209
高阶贝塞尔光束能够携带轨道角动量,且具有无衍射特性,在粒子操控、激光微纳加工及非线性光学等领域具有重要应用价值。目前产生高阶贝塞尔光束的方式无法同时满足集成化和高功率场景的应用需求。基于飞秒激光诱导的双折射纳米光栅结构,提出一种高损伤阈值的集成化光场调控器件制备方法。通过调控纳米光栅的光轴方向和相位延迟量,在石英玻璃内部写入光轴取向空间变化的多层纳米光栅结构,制备的器件可以实现不同光场调控功能的叠加和不同工作波长的设计。基于所提方法制备了中心波长为532 nm、拓扑荷值为4的高阶贝塞尔光束产生器件。器件产生的高阶贝塞尔光束携带的轨道角动量与设计值相符,在4 m距离内光斑大小保持基本不变。器件的零几率激光损伤阈值为28.5 J/cm2(6 ns),在高功率激光光束整形等领域具有极大的应用潜力。
激光光场调控 高阶贝塞尔光束 集成化光学元件 飞秒激光 纳米光栅 激光损伤阈值 光学学报
2023, 43(13): 1326003
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laser Micro/Nano Fabrication Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an 710119, China
3 Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln, Nebraska 68588-0511, USA
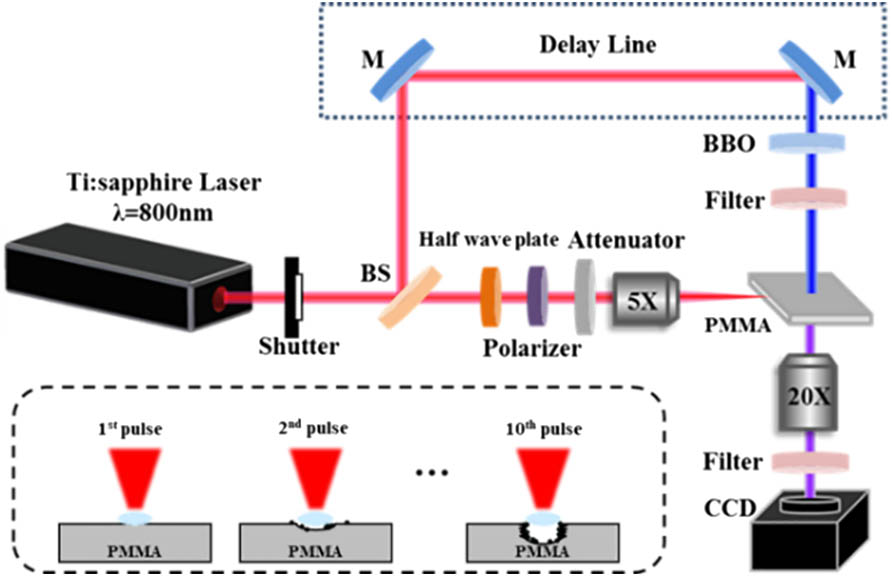
Cylindrical shockwaves inside polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) generated simultaneously with two hemispherical shockwaves induced by a femtosecond Gaussian beam laser were investigated using an ultrafast pump–probe imaging technique. The evolutions of these three shockwaves with probe delay and incident pulse number have been systematically analyzed. The plasma intensity and filament length in the center of cylindrical shockwave both decayed with pulse number. Moreover, the self-focused filament moved downstream towards the output surface with an increased pulse number. The experimental results and mechanism illustrated that energy deposition was suppressed by a degraded nonlinear effect due to a pre-ablated structure in multi-pulse irradiation.
140.7090 Ultrafast lasers 320.7120 Ultrafast phenomena 350.5400 Plasmas 350.3390 Laser materials processing Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(8): 081405

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laser Micro/Nano Fabrication Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 Laser Thermal Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of California, Berkeley, California 94720, USA
3 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln, Nebraska 68588-0511, USA
The dynamics of plasma and shockwave expansion during two femtosecond laser pulse ablation of fused silica are studied using a time-resolved shadowgraph imaging technique. The experimental results reveal that during the second pulse irradiation on the crater induced by the first pulse, the expansion of the plasma and shockwave is enhanced in the longitudinal direction. The plasma model and Fresnel diffraction theory are combined to calculate the laser intensity distribution by considering the change in surface morphology and transient material properties. The theoretical results show that after the free electron density induced by the rising edge of the pulse reaches the critical density, the originally transparent surface is transformed into a transient high-reflectivity surface (metallic state). Thus, the crater with a concave-lens-like morphology can tremendously reflect and refocus the latter part of the laser pulse, leading to a strong laser field with an intensity even higher than the incident intensity. This strong refocused laser pulse results in a stronger laser-induced air breakdown and enhances the subsequent expansion of the plasma and shockwave. In addition, similar shadowgraphs are also recorded in the single-pulse ablation of a concave microlens, providing experimental evidence for the enhancement mechanism.
(320.7100) Ultrafast measurements (140.3390) Laser materials processing (140.3440) Laser-induced breakdown. Photonics Research
2017, 5(5): 05000488
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Laser Micro/Nano Fabrication Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
An interesting transition between low spatial frequency laser-induced periodic surface structure (LIPSS) and high spatial frequency LIPSS (HSFL) on the surface of nickel is revealed by changing the scanning speed and the laser fluence. The experimental results show the proportion of HSFL area in the overall LIPSS (i.e., K) presents a quasi-parabola function trend with the polarization orientation under a femtosecond (fs) laser single-pulse train. Moreover, an obvious fluctuation dependence of K on the pulse delay is observed under a fs laser dual-pulse train. The peak value of the fluctuation is found to be determined by the polarization orientation of the dual-pulse train.
220.4241 Nanostructure fabrication 320.2250 Femtosecond phenomena 260.5430 Polarization 320.5540 Pulse shaping Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(6): 062201





